Overview of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (PM&R)
What is PM&R?
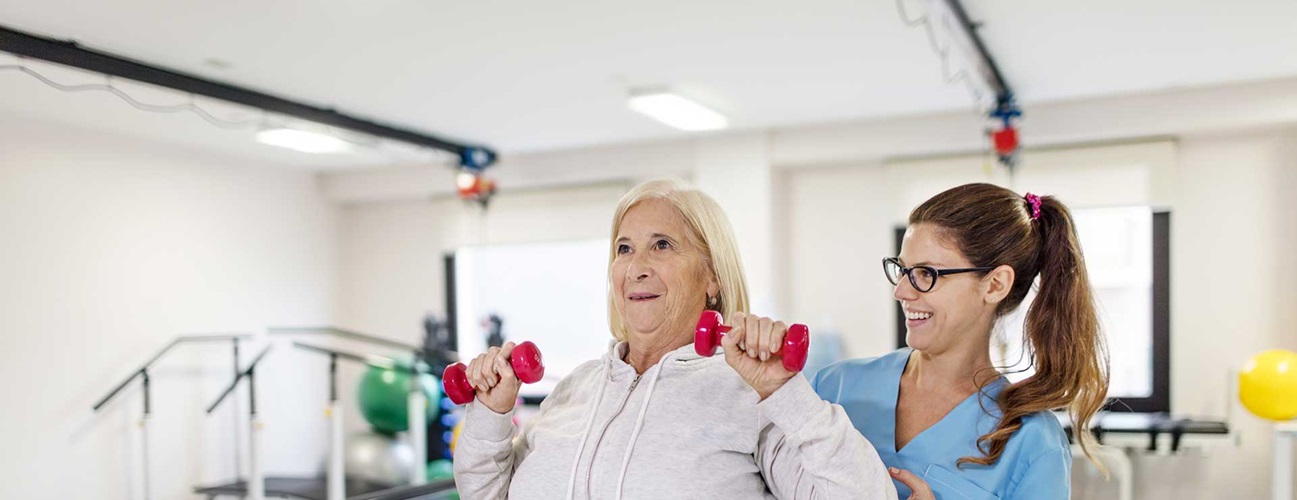
Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (PM&R), also known as physiatry, is a medical specialty that involves restoring function for a person who has been disabled as a result of a disease, disorder, or injury.
Physiatry provides integrated, multidisciplinary care aimed at recovery of the whole person by addressing the individual's physical, emotional, medical, vocational, and social needs. A doctor who specializes in physical medicine and rehabilitation is called a physiatrist.
What is rehabilitation?
Rehabilitation is the process of helping a person achieve the highest level of function, independence, and quality of life possible. Rehab does not reverse or undo the damage caused by disease or injury, but rather helps restore the person to optimal health, functioning, and well-being. Rehabilitate means to make able.
The rehabilitation program
Rehabilitation medicine is designed to meet each person's specific needs; therefore, each program is different. Some general treatment components for rehab programs include:
-
Treating the basic disease and preventing complications
-
Treating the disability and improving function
-
Providing adaptive tools and altering the environment
-
Teaching the patient and family and helping them adapt to lifestyle changes
The success of rehab depends on many variables, including:
-
The nature and severity of the disease, disorder, or injury
-
The type and degree of any resulting impairments and disabilities
-
The overall health of the patient
-
Family support
Areas covered in rehabilitation programs may include the following:
| Patient need | Example |
|---|---|
| Self-care skills, including activities of daily living (ADLs) | Feeding, grooming, bathing, dressing, toileting, and sexual function |
| Physical care | Nutritional needs, medicine, and skin care |
| Mobility skills | Walking, transfers, and self-propelling a wheelchair |
| Respiratory care | Ventilator care, if needed; breathing treatments and exercises to promote lung function |
| Communication skills | Speech, writing, and alternative methods of communication |
| Cognitive skills | Memory, concentration, judgment, problem-solving, and organizational skills |
| Socialization skills | Interacting with others at home and within the community |
| Vocational training | Work-related skills |
| Pain management | Medicine and alternative methods of managing pain |
| Psychological counseling | Identifying problems and solutions with thinking, behavioral, and emotional issues |
| Family support | Assistance with adapting to lifestyle changes, financial concerns, and discharge planning |
| Education | Patient and family education and training about the condition, medical care, and adaptive techniques |
Understanding rehabilitation terminology
Rehabilitation is needed when a disease and injury causes an impairment. Consider the following:
-
An impairment is a loss of normal function of part of the body, such as paralysis of a leg.
-
Disability occurs when a person is not able to perform an activity in a normal way as a result of an impairment, such as not being able to walk.
-
A handicap occurs when there are limits that prevent a person with a disability from performing a role that is normal for that person, such as not being able to work. A handicap refers to a barrier that may be imposed by society, the environment, or by one's own attitude.
Most people with disabilities are not considered handicapped. They go to school, work, perform family duties, and interact with society fully and capably.